Investigation on Hydrodynamics of Fish Swimming
Simulation and Workflow
The simulation of fluid-solid coupling is achieved by immersed boundary-lattice Boltzmann method based on the open source software Palabos, where a harmonic wave is applied to the fish body to achieve the motion of fish swimming. The simulation results are analyzed by dynamic mode decomposition to study the spatiotemporal dynamics of fish swimming.
Workflow:
- The fish mesh is reconstructed from point clouds generated by fitting functions for the fish body.
- Conduct grid independence study and validate the algorithm by benchmark cases such as flow passing oscillating and static spheres.
- Visualize simulation results and use Q-criterion to extract vortex structures for flow pattern investigation.
- Apply dynamic mode decomposition on the fluid data to reveal the hidden dynamics of fish swimming.
The simulated fish swimming:

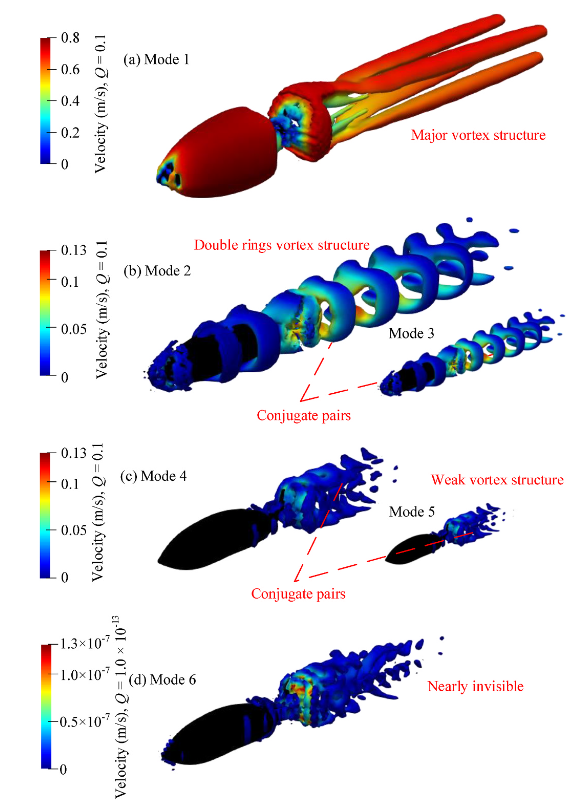
The reconstructed vortex structures by dynamic modes:
Publications
- Fang, Dehong, et al. "Flow pattern investigation of bionic fish by immersed boundary–lattice Boltzmann method and dynamic mode decomposition." Ocean Engineering 248 (2022): 110823.
- Fang, D., et al. "Effect of fish swimming on the stability of flow fields inside the pipeline." IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. Vol. 1037. No. 1. IOP Publishing, 2022.
- Fang, Dehong, Jinsong Zhang, and Zhenwei Huang. "Modal analysis on mechanism of bionic fish swimming by dynamic mode decomposition." Ocean Engineering 273 (2023): 113897.
- Fang, Dehong, et al. "Immersed force analysis of fish surface with carangiform locomotion." Physics of Fluids 36.3 (2024).
